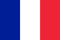
Prostatitis is a disease that can suddenly overwhelm any man.
The urinary tract passes through the prostate gland, which contributes to the complication of one of the first symptoms of the disease - urinary excretion.
Prostatitis - the beginning
The onset of the disease is always associated with certain conditions of our lives.
There are several types of prostatitis:
- Sharp;
- Chronic;
- Infectious (bacterial);
- Non-infectious.

Nomenclature, in this case, dual, for example, infectious prostatitis can be chronic and acute.
Each type of prostatitis will start differently and will initially be selected according to its individual conditions. Let's look at them.
Risk factors, conditions of occurrence
- STD. When a man is infected with any sexually transmitted infection from a sexual partner, the man has a great chance of catching an acute infectious prostate, which can later turn into a chronic disease. Thus, sexually transmitted diseases will be the first factor prone to prostatitis.
- Sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, apathy to sports and morning exercises, obesity. This is the cause of non-infectious prostatitis, which can be exacerbated or present with vague symptoms.
- Hypothermia - In this condition, the genitourinary system is often exposed to cold attacks, which can result in inflammation of the bladder, seminal vesicles, prostate gland and testicles.
- Age. When a man reaches the age of 40-45, irreversible changes in the prostate gland begin. This is due to male menopause - a direct result of hormonal restructuring in the body. As the prostate grows (hyperplasia), all the symptoms of prostatitis are accompanied (or may be accompanied) by a palette.
To summarize - these factors increase the chances of getting prostatitis tenfold.

Next, let's look at the first signs of different types of prostatitis.
Before making a self-diagnosis or panicking to contact a doctor when the first symptoms appear - pay attention to the above risk factors. Maybe you don't have prostatitis!
Symptoms
Acute process
It should be noted that the first symptoms of acute prostatitis are often similar in all patients:
- Pain when urinating, then burning;
- Temperature rise;
- After heroically emptying the bladder, the patient feels that there is still urine inside;
- Complaints of pain in the groin and perineum.
The pain starts suddenly, and there are problems with the toilet. This is due to the rapid increase in inflammation of the inflamed prostate.
Symptoms may disappear on their own, but do not create the illusion: this does not mean that the disease has passed.
Prostatitis becomes chronic. It can take a long time (years) from the first symptoms of acute prostatitis to the onset of chronic prostatitis.
Chronic process
Perhaps the patient did not have an acute period, and the disease bypassed him and became a chronic form.
In this case, the symptoms will be as follows:
- Dull pain in the anus after bowel movements spreads to the tailbone;
- Regular or irregular groin pain;
- Going to the bathroom isn't particularly difficult, but you have to strain the culture a bit to start urinating. The patient does not pay much attention to it;
- Occasionally there is a burning sensation in the urethra after urination.
The first signs of chronic prostatitis may appear over a long period of time. They may disappear, and then they feel again.
Infectious prostatitis
Often, patients with infectious prostatitis also carry other sexually transmitted diseases.
Among the first signs should be noted:
- Incision in the urethra, blood in the urine;
- Temperature rise;
- Clear urine (pus)
- The desire to use the toilet often.
The first symptoms of bacterial prostatitis are similar to acute prostatitis, because the latter type often occurs as a result of the efforts of a specific infectious agent.

Non-infectious prostatitis
After 40 years, a man may find the first signs of non-infectious prostatitis. It's not the bacteria's fault, it's just the time.
The prostate grows, may manifest itself in some way, or may go unnoticed.
If a man has a problem, it boils down to the following manifestations:
- Has difficulty urinating
- The amount of residual urine in the bladder.

If it causes inflammation of the prostate, pain, burning, and possibly fever are added.
Any prostatitis has the main (main) manifestations in problems with urination. The pain may be of different localization and intensity, burning at the end of urination and after absence.
Sexual problems occur in 100 to 99% of cases, but this period is long, lasting several years or more.
Among the first symptoms is a decrease in urinary pressure. If you need to strain your abdomen to start urinating (even if you don't care), it's time to see a urologist.
This is the first sign of impending prostatitis.
What if you ignore all these symptoms?
Let's say that acute prostatitis goes away on its own (let's imagine it comes).
After a few days of suffering, we easily go to the toilet again, and the burning sensation and pain left us.
The euphoria will not last long - chronic inflammation closes the prostate, so prostatitis still reminds itself.
This is not the worst thing, because you can live with such sensations. What is important is what happens inside the prostate gland.
Let's remember what it does - to protect the vital activity of sperm.
Prostatitis inhibits and blocks this function. As a result of advanced prostatitis, a man may lose the ability to conceive.

Another unpleasant consequence of advanced prostatitis is depression and bad mood. Frequent toilet problems add stress to a man.
Incomplete emptying of the bladder causes inflammatory processes in it and in other parts of the urinary system.
So do not be idle.
How is prostatitis diagnosed?
Contact your urologist at the first sign of illness and tell us how you feel.
Prostatitis is diagnosed by medical history, rectal examination of the prostate and TRUS.
The remaining methods are used to identify or rule out concomitant diseases as an additional disease.
You can diagnose at home. However, prostatitis can be confused with inflammation of the urethra or bladder, so read the diagnosis of prostatitis carefully.
Treatment
Treatment of prostatitis depends on its form.
The main responsibilities of the doctor:
- Restoration of a normal ureter. It is necessary to reduce swelling, eliminate muscle spasms and stimulate urine production and excretion.
- Fighting an infectious agent or physically eliminating the cause of prostatitis.
- Relapse prevention (diet, lifestyle and good habits).
- Stimulation of the prostate gland - rectal massage of the prostate.
You can also be treated at home by agreeing on treatment methods with a urologist. For example, it is useful to put special microclysters containing herbal decoctions.
Your doctor will prescribe physiotherapy to speed recovery.